Medical Named Entity Recognition
Medical named entity recognition is the process of identifying and categorizing medical terms or entities in text data.
Papers and Code
Semantic NLP Pipelines for Interoperable Patient Digital Twins from Unstructured EHRs
Jan 09, 2026Digital twins -- virtual replicas of physical entities -- are gaining traction in healthcare for personalized monitoring, predictive modeling, and clinical decision support. However, generating interoperable patient digital twins from unstructured electronic health records (EHRs) remains challenging due to variability in clinical documentation and lack of standardized mappings. This paper presents a semantic NLP-driven pipeline that transforms free-text EHR notes into FHIR-compliant digital twin representations. The pipeline leverages named entity recognition (NER) to extract clinical concepts, concept normalization to map entities to SNOMED-CT or ICD-10, and relation extraction to capture structured associations between conditions, medications, and observations. Evaluation on MIMIC-IV Clinical Database Demo with validation against MIMIC-IV-on-FHIR reference mappings demonstrates high F1-scores for entity and relation extraction, with improved schema completeness and interoperability compared to baseline methods.
Scalable Construction of a Lung Cancer Knowledge Base: Profiling Semantic Reasoning in LLMs
Jan 05, 2026The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into biomedical research offers new opportunities for domainspecific reasoning and knowledge representation. However, their performance depends heavily on the semantic quality of training data. In oncology, where precision and interpretability are vital, scalable methods for constructing structured knowledge bases are essential for effective fine-tuning. This study presents a pipeline for developing a lung cancer knowledge base using Open Information Extraction (OpenIE). The process includes: (1) identifying medical concepts with the MeSH thesaurus; (2) filtering open-access PubMed literature with permissive licenses (CC0); (3) extracting (subject, relation, object) triplets using OpenIE method; and (4) enriching triplet sets with Named Entity Recognition (NER) to ensure biomedical relevance. The resulting triplet sets provide a domain-specific, large-scale, and noise-aware resource for fine-tuning LLMs. We evaluated T5 models finetuned on this dataset through Supervised Semantic Fine-Tuning. Comparative assessments with ROUGE and BERTScore show significantly improved performance and semantic coherence, demonstrating the potential of OpenIE-derived resources as scalable, low-cost solutions for enhancing biomedical NLP.
Faithful Summarization of Consumer Health Queries: A Cross-Lingual Framework with LLMs
Nov 13, 2025Summarizing consumer health questions (CHQs) can ease communication in healthcare, but unfaithful summaries that misrepresent medical details pose serious risks. We propose a framework that combines TextRank-based sentence extraction and medical named entity recognition with large language models (LLMs) to enhance faithfulness in medical text summarization. In our experiments, we fine-tuned the LLaMA-2-7B model on the MeQSum (English) and BanglaCHQ-Summ (Bangla) datasets, achieving consistent improvements across quality (ROUGE, BERTScore, readability) and faithfulness (SummaC, AlignScore) metrics, and outperforming zero-shot baselines and prior systems. Human evaluation further shows that over 80\% of generated summaries preserve critical medical information. These results highlight faithfulness as an essential dimension for reliable medical summarization and demonstrate the potential of our approach for safer deployment of LLMs in healthcare contexts.
AfriSpeech-MultiBench: A Verticalized Multidomain Multicountry Benchmark Suite for African Accented English ASR
Nov 18, 2025Recent advances in speech-enabled AI, including Google's NotebookLM and OpenAI's speech-to-speech API, are driving widespread interest in voice interfaces globally. Despite this momentum, there exists no publicly available application-specific model evaluation that caters to Africa's linguistic diversity. We present AfriSpeech-MultiBench, the first domain-specific evaluation suite for over 100 African English accents across 10+ countries and seven application domains: Finance, Legal, Medical, General dialogue, Call Center, Named Entities and Hallucination Robustness. We benchmark a diverse range of open, closed, unimodal ASR and multimodal LLM-based speech recognition systems using both spontaneous and non-spontaneous speech conversation drawn from various open African accented English speech datasets. Our empirical analysis reveals systematic variation: open-source ASR models excels in spontaneous speech contexts but degrades on noisy, non-native dialogue; multimodal LLMs are more accent-robust yet struggle with domain-specific named entities; proprietary models deliver high accuracy on clean speech but vary significantly by country and domain. Models fine-tuned on African English achieve competitive accuracy with lower latency, a practical advantage for deployment, hallucinations still remain a big problem for most SOTA models. By releasing this comprehensive benchmark, we empower practitioners and researchers to select voice technologies suited to African use-cases, fostering inclusive voice applications for underserved communities.
MedPath: Multi-Domain Cross-Vocabulary Hierarchical Paths for Biomedical Entity Linking
Nov 14, 2025Progress in biomedical Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Entity Linking (EL) is currently hindered by a fragmented data landscape, a lack of resources for building explainable models, and the limitations of semantically-blind evaluation metrics. To address these challenges, we present MedPath, a large-scale and multi-domain biomedical EL dataset that builds upon nine existing expert-annotated EL datasets. In MedPath, all entities are 1) normalized using the latest version of the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS), 2) augmented with mappings to 62 other biomedical vocabularies and, crucially, 3) enriched with full ontological paths -- i.e., from general to specific -- in up to 11 biomedical vocabularies. MedPath directly enables new research frontiers in biomedical NLP, facilitating training and evaluation of semantic-rich and interpretable EL systems, and the development of the next generation of interoperable and explainable clinical NLP models.
Multilingual BERT language model for medical tasks: Evaluation on domain-specific adaptation and cross-linguality
Oct 31, 2025In multilingual healthcare applications, the availability of domain-specific natural language processing(NLP) tools is limited, especially for low-resource languages. Although multilingual bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) offers a promising motivation to mitigate the language gap, the medical NLP tasks in low-resource languages are still underexplored. Therefore, this study investigates how further pre-training on domain-specific corpora affects model performance on medical tasks, focusing on three languages: Dutch, Romanian and Spanish. In terms of further pre-training, we conducted four experiments to create medical domain models. Then, these models were fine-tuned on three downstream tasks: Automated patient screening in Dutch clinical notes, named entity recognition in Romanian and Spanish clinical notes. Results show that domain adaptation significantly enhanced task performance. Furthermore, further differentiation of domains, e.g. clinical and general biomedical domains, resulted in diverse performances. The clinical domain-adapted model outperformed the more general biomedical domain-adapted model. Moreover, we observed evidence of cross-lingual transferability. Moreover, we also conducted further investigations to explore potential reasons contributing to these performance differences. These findings highlight the feasibility of domain adaptation and cross-lingual ability in medical NLP. Within the low-resource language settings, these findings can provide meaningful guidance for developing multilingual medical NLP systems to mitigate the lack of training data and thereby improve the model performance.
DICOM De-Identification via Hybrid AI and Rule-Based Framework for Scalable, Uncertainty-Aware Redaction
Jul 31, 2025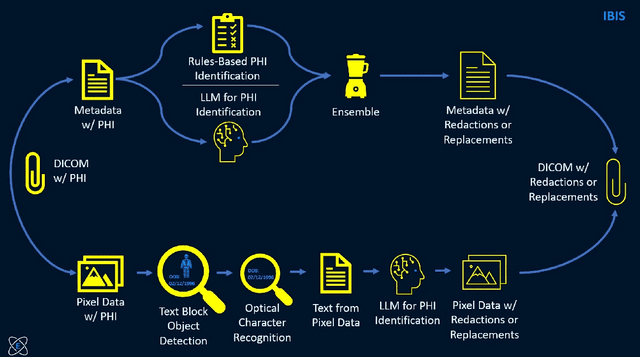
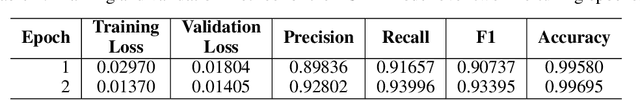

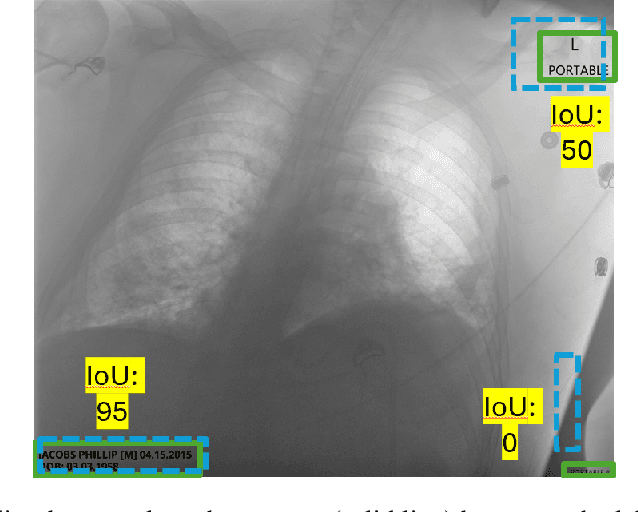
Access to medical imaging and associated text data has the potential to drive major advances in healthcare research and patient outcomes. However, the presence of Protected Health Information (PHI) and Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) files presents a significant barrier to the ethical and secure sharing of imaging datasets. This paper presents a hybrid de-identification framework developed by Impact Business Information Solutions (IBIS) that combines rule-based and AI-driven techniques, and rigorous uncertainty quantification for comprehensive PHI/PII removal from both metadata and pixel data. Our approach begins with a two-tiered rule-based system targeting explicit and inferred metadata elements, further augmented by a large language model (LLM) fine-tuned for Named Entity Recognition (NER), and trained on a suite of synthetic datasets simulating realistic clinical PHI/PII. For pixel data, we employ an uncertainty-aware Faster R-CNN model to localize embedded text, extract candidate PHI via Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and apply the NER pipeline for final redaction. Crucially, uncertainty quantification provides confidence measures for AI-based detections to enhance automation reliability and enable informed human-in-the-loop verification to manage residual risks. This uncertainty-aware deidentification framework achieves robust performance across benchmark datasets and regulatory standards, including DICOM, HIPAA, and TCIA compliance metrics. By combining scalable automation, uncertainty quantification, and rigorous quality assurance, our solution addresses critical challenges in medical data de-identification and supports the secure, ethical, and trustworthy release of imaging data for research.
LLM-based Prompt Ensemble for Reliable Medical Entity Recognition from EHRs
May 13, 2025Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital records of patient information, often containing unstructured clinical text. Named Entity Recognition (NER) is essential in EHRs for extracting key medical entities like problems, tests, and treatments to support downstream clinical applications. This paper explores prompt-based medical entity recognition using large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1, guided by various prompt engineering techniques, including zero-shot, few-shot, and an ensemble approach. Among all strategies, GPT-4o with prompt ensemble achieved the highest classification performance with an F1-score of 0.95 and recall of 0.98, outperforming DeepSeek-R1 on the task. The ensemble method improved reliability by aggregating outputs through embedding-based similarity and majority voting.
Automatic Posology Structuration : What role for LLMs?
Jun 24, 2025Automatically structuring posology instructions is essential for improving medication safety and enabling clinical decision support. In French prescriptions, these instructions are often ambiguous, irregular, or colloquial, limiting the effectiveness of classic ML pipelines. We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to convert free-text posologies into structured formats, comparing prompt-based methods and fine-tuning against a "pre-LLM" system based on Named Entity Recognition and Linking (NERL). Our results show that while prompting improves performance, only fine-tuned LLMs match the accuracy of the baseline. Through error analysis, we observe complementary strengths: NERL offers structural precision, while LLMs better handle semantic nuances. Based on this, we propose a hybrid pipeline that routes low-confidence cases from NERL (<0.8) to the LLM, selecting outputs based on confidence scores. This strategy achieves 91% structuration accuracy while minimizing latency and compute. Our results show that this hybrid approach improves structuration accuracy while limiting computational cost, offering a scalable solution for real-world clinical use.
Pre-trained Language Models and Few-shot Learning for Medical Entity Extraction
Apr 06, 2025This study proposes a medical entity extraction method based on Transformer to enhance the information extraction capability of medical literature. Considering the professionalism and complexity of medical texts, we compare the performance of different pre-trained language models (BERT, BioBERT, PubMedBERT, ClinicalBERT) in medical entity extraction tasks. Experimental results show that PubMedBERT achieves the best performance (F1-score = 88.8%), indicating that a language model pre-trained on biomedical literature is more effective in the medical domain. In addition, we analyze the impact of different entity extraction methods (CRF, Span-based, Seq2Seq) and find that the Span-based approach performs best in medical entity extraction tasks (F1-score = 88.6%). It demonstrates superior accuracy in identifying entity boundaries. In low-resource scenarios, we further explore the application of Few-shot Learning in medical entity extraction. Experimental results show that even with only 10-shot training samples, the model achieves an F1-score of 79.1%, verifying the effectiveness of Few-shot Learning under limited data conditions. This study confirms that the combination of pre-trained language models and Few-shot Learning can enhance the accuracy of medical entity extraction. Future research can integrate knowledge graphs and active learning strategies to improve the model's generalization and stability, providing a more effective solution for medical NLP research. Keywords- Natural Language Processing, medical named entity recognition, pre-trained language model, Few-shot Learning, information extraction, deep learning
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge